-
 Industry News- In which industries is SF-2 Boundary Self-Lubricating...
Industry News- In which industries is SF-2 Boundary Self-Lubricating...SF-2 Boundary Self-Lubricating Bearing is a high-performance self-lubricating bearing that is widely used in multiple industries due to its ...
-
 Industry News- What are the characteristics of industrial automation...
Industry News- What are the characteristics of industrial automation...The demand for solid lubricant bearings in the field of industrial automation has unique characteristics, which are mainly derived from the ...
-
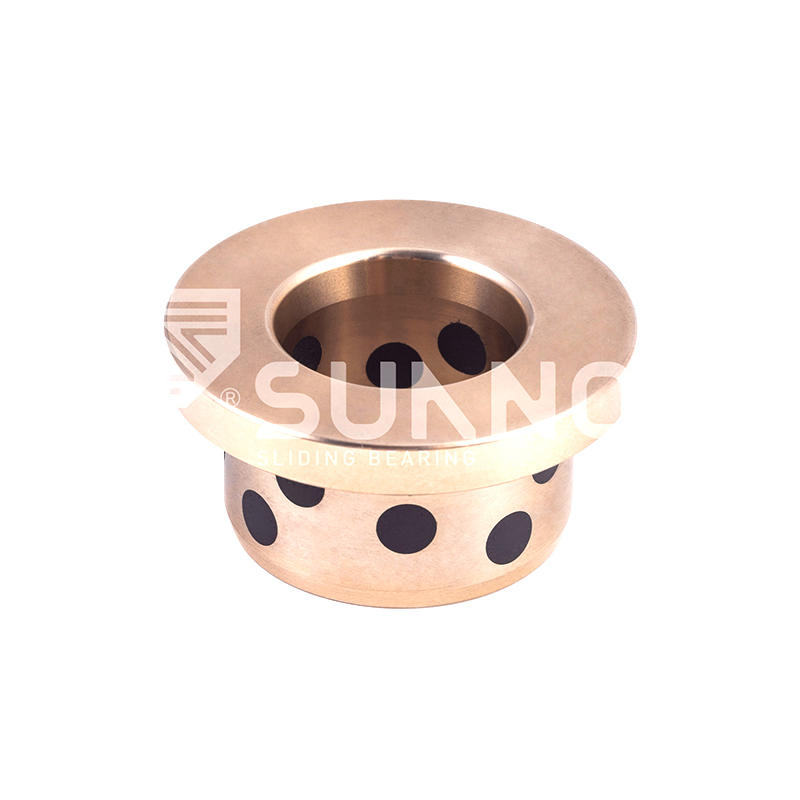 Industry News- What are the main drivers of the growth of the solid ...
Industry News- What are the main drivers of the growth of the solid ...1. Promotion of environmental regulationsWith the global emphasis on environmental protection, countries have introduced strict environmenta...
-
 Industry News- Innovative application of solid lubrication bearings ...
Industry News- Innovative application of solid lubrication bearings ...1. Technical backgroundWith the rapid development of the new energy vehicle industry, higher requirements are placed on the performance of c...
-
 Industry News- SF-2 Boundary Self-Lubricating Bearing: A new choice ...
Industry News- SF-2 Boundary Self-Lubricating Bearing: A new choice ...SF-2 Boundary Self-Lubricating Bearing is a boundary lubricating bearing made of three-layer composite self-lubricating material. The follow...
-
0+Establishment
Founded in 2014, Shuangnuo has 10 years of experience in the industry.
-
0+Advanced Equipment
Strong production capacity ensures that we can organize material production for customers as soon as possible and shorten the production cycle.
-
0+Happy Clients
There are more than 5,000 cooperative customers around the world.
What are the key steps in the production process of self-lubricating copper alloy bearings?
The production process of self-lubricating copper alloy bearings involves multiple precision steps to ensure that the bearings have excellent mechanical properties, wear resistance and self-lubricating properties. The following are the key steps in its production process:
1. Copper alloy ingredients and smelting
Raw material selection: According to the application requirements, select the appropriate copper alloy type (such as bronze, aluminum bronze, copper-lead alloy, etc.), and other alloying elements such as tin, aluminum, zinc, and lead may be added to improve the characteristics.
Smelting: The selected copper alloy material is melted to the appropriate temperature to ensure uniform distribution, and the temperature and impurity content during the smelting process are strictly controlled to ensure the purity and mechanical properties of the alloy.
2. Casting
Gravity casting or centrifugal casting: The molten copper alloy is poured into the mold through gravity casting or centrifugal casting process to form a preliminary bearing blank. Centrifugal casting is suitable for manufacturing round, hollow parts, which can improve the density and fatigue resistance of the material.
Cooling and demolding: The cast blank is demolded after cooling to ensure that there are no cracks or other casting defects.
3. Machining
Turning and milling: The bearing blank is precisely machined by **CNC machine tools** to achieve the design size and tolerance. This step ensures the shape, inner and outer diameter accuracy and surface finish of the bearing.
Drilling or slotting: Lubrication grooves or holes are machined on the bearing surface to embed solid lubricants. These structures can help the lubricant to be better distributed and improve the self-lubricating performance of the bearing.
4. Solid lubricant embedding
Lubricant selection: Different types of solid lubricants such as graphite, molybdenum disulfide, PTFE, etc. are selected according to the working environment and requirements of the bearing.
Embedding process: The solid lubricant is evenly embedded in the lubrication holes or lubrication grooves on the bearing surface through high-temperature sintering or press-embed technology. This is a key step to ensure that the bearing has long-term self-lubricating performance.
5. Sintering and shaping
In some cases, the bearings embedded with lubricants will be sintered to make the copper alloy and lubricant more closely combined, and the dimensional accuracy of the product is guaranteed by the shaping process.
6. Surface treatment
Polishing and grinding: Precision polishing and grinding of the inner and outer surfaces of the bearing to further improve the surface finish and reduce the friction coefficient.
Surface protection: Depending on the application requirements, the bearing may be surface treated, such as tin plating, nickel plating, etc., to enhance its corrosion resistance and extend its service life.
7. Quality inspection
Dimensional accuracy inspection: Use a three-dimensional coordinate measuring machine or laser measuring equipment to check the key dimensions and tolerances of the bearing to ensure that they meet the design specifications.
Performance testing: Test the friction coefficient, wear resistance, load capacity and other performance to ensure that the bearing meets industry standards in terms of self-lubricating performance, wear resistance and other aspects.
8. Cleaning and packaging
Ultrasonic cleaning: Clean the bearing to remove impurities, oil or other contaminants that may remain during the production process.
Rust-proof packaging: The cleaned bearings are treated with rust-proof oil and protectively packaged according to customer requirements to ensure that they will not be damaged or corroded during transportation and storage.
9. Final inspection and shipment
Before shipment, all products must undergo a final appearance and performance inspection to ensure that each bearing meets the predetermined technical standards.